Today we learned how to use "for" and "since" with present perfect.
We use "for" to talk about a period of time (duration).
It answers the question "how long"?
He has had this car for three years.
We use "since" to talk about a specific time in the past.
It tells us when something first happened.
He has had this car since 2013.
Try this exercise to choose "for" or "since".
Another one
This one, too!
One more
This too!
On this page you can find links to many more exercises to practice.
lunes, 29 de febrero de 2016
sábado, 27 de febrero de 2016
My project!
Here is my example for the architecture project.
This is the Iglesia de San Miguel in Arcones, Segovia.

It was built in the 13th Century AD. It is in the Romanesque style. It has thick walls and small windows. It is made of stone and has some doors and a window with a rounded arch.


The original structure has been modified in some ways but it still has some original elements.
This is the Iglesia de San Miguel in Arcones, Segovia.

It was built in the 13th Century AD. It is in the Romanesque style. It has thick walls and small windows. It is made of stone and has some doors and a window with a rounded arch.


The original structure has been modified in some ways but it still has some original elements.
Cells, tissues, and systems
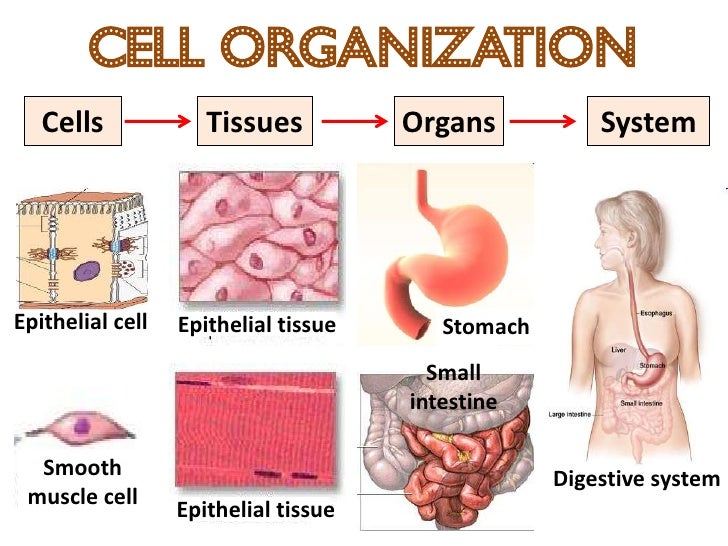
Watch this presentation. It has some very nice pictures of cells and some good explanations (you don't have to know all of the information-- only what is in the book!)
Cells from Alexis Neo
viernes, 26 de febrero de 2016
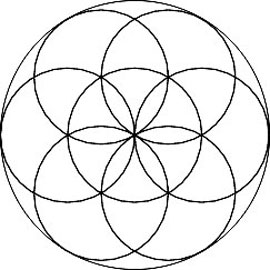
Drawing the Seed of Life
Now that we know how to draw the Flower of Life, you can try to draw the Seed of Life.
jueves, 25 de febrero de 2016
Three cultures of Alcalá de Henares
Did you know that in the Middle Ages, Alcalá was home to three cultures: Christianity, Islam, and Judaism? For much of this time, the three cultures coexisted peacefully.

Do you know where these signs are in our city?

Here you can read about the neighborhoods (in Spanish):
La alijama (Jewish quarters)
La morería (Muslim neighborhood)
The Christian city
This is from the webpage of the City Hall. You can find more information there about the history of Alcalá during the Middle Ages!

Do you know where these signs are in our city?

Here you can read about the neighborhoods (in Spanish):
La alijama (Jewish quarters)
La morería (Muslim neighborhood)
The Christian city
This is from the webpage of the City Hall. You can find more information there about the history of Alcalá during the Middle Ages!
martes, 23 de febrero de 2016
Now it's your turn!
Now you have to find information about a church in Spain. It can be a small church from a village or a big cathedral. Give information about it:
--Where is it?
--When was it built?
--What architectural style is it?
--What are the characteristics of this style?
Put your information on an A4 card (cartulina tamaño folio) and include pictures!
Due: Tuesday, 1st of March.
--Where is it?
--When was it built?
--What architectural style is it?
--What are the characteristics of this style?
Put your information on an A4 card (cartulina tamaño folio) and include pictures!
Due: Tuesday, 1st of March.
Architecture: Vaulting
Your book talks about "barrel vaults" (Romanesque) and "ribbed vaults" (Gothic). But, what does that mean? Here are some pictures:
Barrel vault:


Ribbed vault:


Barrel vault:


Ribbed vault:


lunes, 22 de febrero de 2016
Looking at cells
Plant cells: watch the chloroplasts move!
Here is a short video about onion cells under a microscope.
Animal cells: frog's blood. You can see the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane.
Here is a short video about onion cells under a microscope.
Animal cells: frog's blood. You can see the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane.
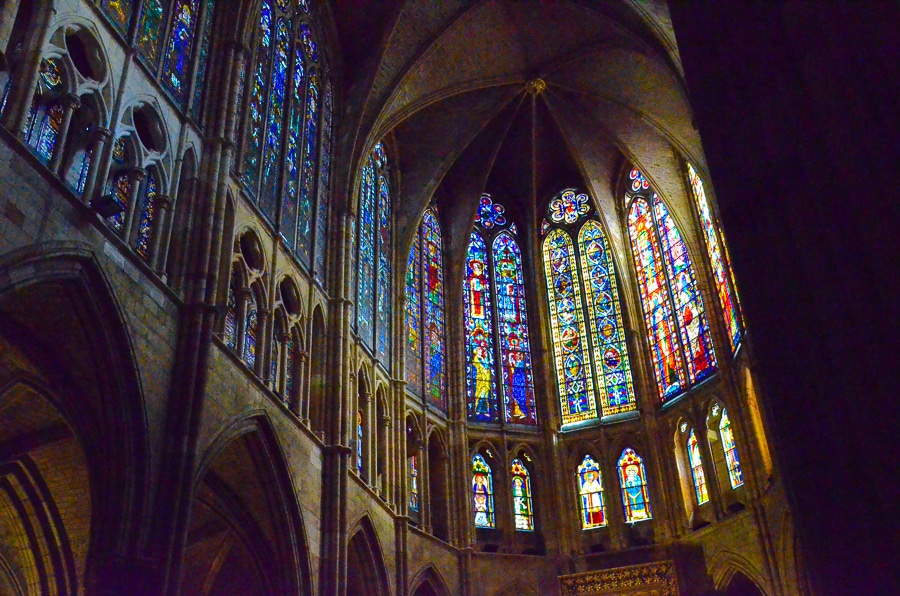
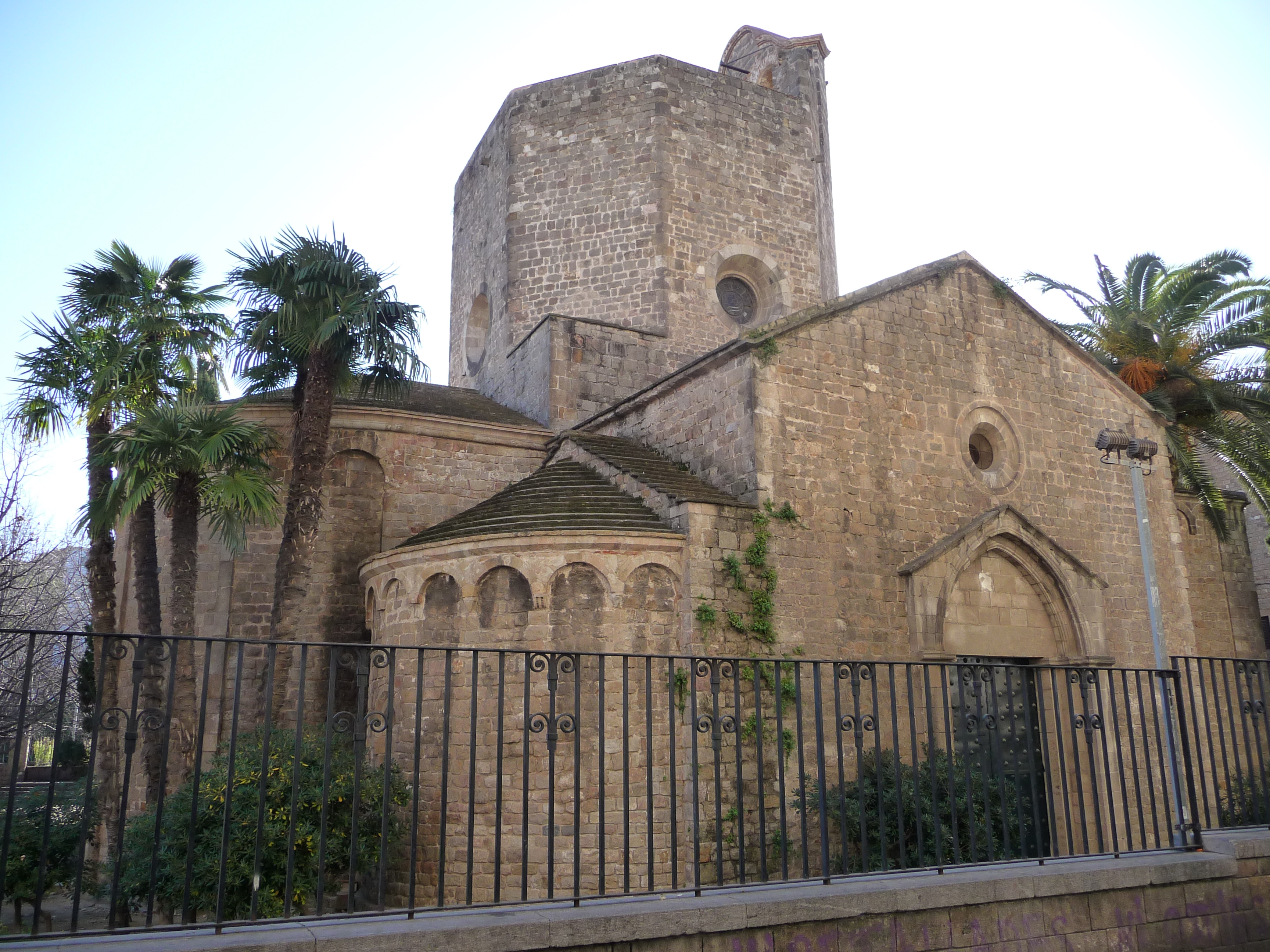
Romanesque vs. Gothic Architecture
In Spain, many Romanesque churches, monasteries, and cathedrals were built between the 11th century and the mid-12th century.




Here are some of the characteristics:
--Stone replaces wood as the main construction material.
--Buildings had thick walls and not many windows. The windows were small.
--The arches were semicircular.
--They used barrel vaults.
--They used barrel vaults.
Here is a Romanesque church, San Martin de Tours, in Palencia.
Gothic Architecture was popular from the 12th century to the 16th century.
Its characteristics:
--Churches were tall and let in a lot of light.
--Walls were thinner and had large, stained-glass windows.
--The pointed arch was used.
--They used ribbed vaults.
--They used ribbed vaults.
Can you find all three of these characteristics in the Cathedral of León?


Do you think these buildings are Romanesque or Gothic?
Monastery of San Pau, Barcelona

Burgos Cathedral, Spain

Frómista, Castilla-León
viernes, 19 de febrero de 2016
Drawing the "flower of life" with a compass
Watch how you can use your compass to create this shape, the Flower of Life.







Islamic Art and tessellations
Islamic Art often used geometric designs and tessellations:
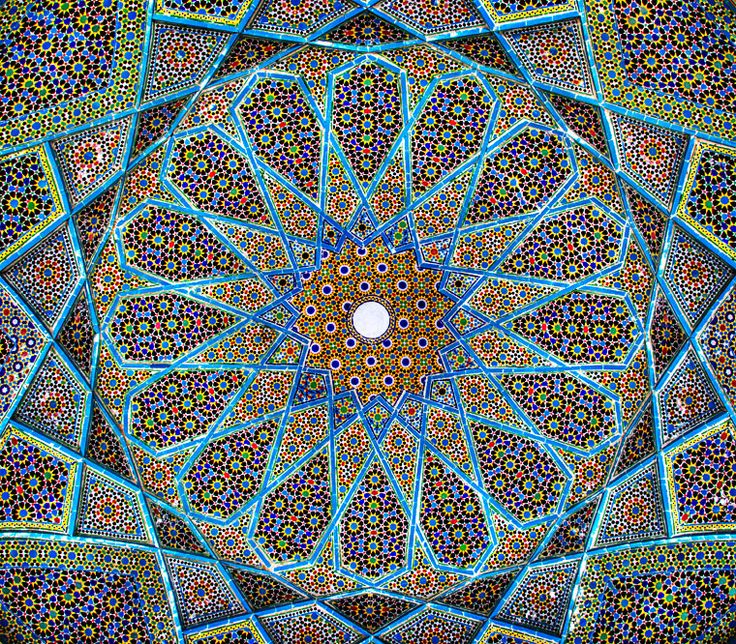



Interactive tessellation creator here.
Some tessellation art projects from a 7th grade in the USA:



Interactive tessellation creator here.
Some tessellation art projects from a 7th grade in the USA:
jueves, 18 de febrero de 2016
Games for English review
Let's review "so" "such" "such a" and "such an."

Here is a game to review.

Here is a game to review.
Now let's review "that" and "which."
Susan watched a film.
The film was very long.
Susan watched a film which was very long.
The film which Susan watched was
very long.
Tom bought a pair of
trainers. They were very expensive.
Tom…
The trainers…
We heard a song. It
was very good.
We…
The song…
Now, adverbs of time.
Can you make sentences with these words? Which verb tense do you need to use for each one?
last week----later-----sometimes----soon----now----yesterday
miércoles, 17 de febrero de 2016
Life in Medieval Society
In the Middle Ages, society was divided into three groups:
--The nobles
--The clergy
--The commoners. We can divide this group into: artisans and merchants (people who made and sold products) and peasants (people who worked on the land growing crops.)

At first, most people were peasants. Later, by the 12th century, cities became very important. The people who lived there were called the bourgeoisie (burgueses). Artisans organised themselves into guilds (gremios).
Play this game to see how much you know about the Medieval Christian society.
This presentation tells you about the Middle Ages (Visigothic Kingdom, Al-Andalus, and Christian Kingdoms.) There are even some short videos!
--The nobles
--The clergy
--The commoners. We can divide this group into: artisans and merchants (people who made and sold products) and peasants (people who worked on the land growing crops.)

At first, most people were peasants. Later, by the 12th century, cities became very important. The people who lived there were called the bourgeoisie (burgueses). Artisans organised themselves into guilds (gremios).
Play this game to see how much you know about the Medieval Christian society.
This presentation tells you about the Middle Ages (Visigothic Kingdom, Al-Andalus, and Christian Kingdoms.) There are even some short videos!
Christian Spain
In 1031, the Caliphate of Cordoba was divided into separate taifas. On this map you can see the different taifas. The kingdoms above the purple line are Christian Kingdoms and the ones below the purple line are the Muslim taifas.
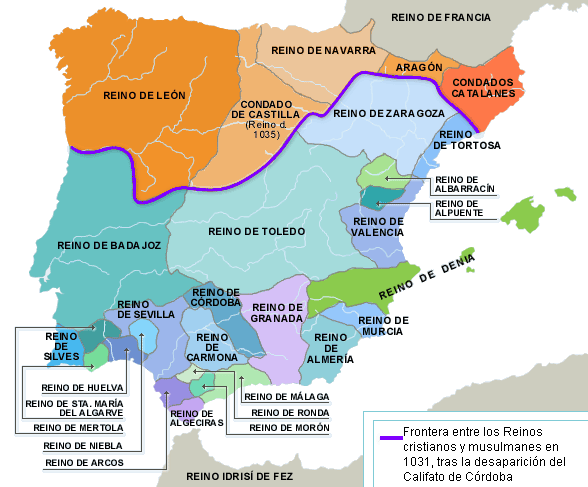
In this map you can see the different stages of the Reconquest (Reconquista.)

The first of the Christian Kingdoms was the Kingdom of Asturias (colour red on the map) in 722 AD. Then the Reconquest moved south little by little until the last Muslim Kingdom, Granada, fell to the Catholic Monarchs in 1492 AD.
Here is a short video (in Spanish) about the Reconquest:
For your test, you need to know these important dates:
722-- Kingdom of Asturias founded.
1212--Battle of Navas de Tolosa. Christian forces win control of much of the southern peninsula.
1492-- Conquest of the Kingdom of Granada by the Catholic Monarchs.
Test time!
Your English Test Unit 6 is on Tuesday. It will include:
--Adverbs (where, when, and how)
--Last 6
verbs on your list
--so/such/
such a/ such an
--sentences
with “that” and “which”
--short
listening
--short
reading comprehension
--present
perfect questions and answers
--general
grammar review
You do not need to study vocabulary this time.
***Your Natural Science Test will be in the first week of March. (A concretar el día más adelante, para no juntar tantos examenes en una sola semana.)*****
Good Luck!
martes, 16 de febrero de 2016
Adverbs!
Adverbs tell us about the verb. It can tell us where, when, or how an action is done.
How: She walked slowly.
Where: He looked over there.
When: We get up early.
On your English test you need to know about adverbs of time (WB p.57) and adverbs of place (WB p. 47)
Here are some songs about adverbs:
How: She walked slowly.
Where: He looked over there.
When: We get up early.
On your English test you need to know about adverbs of time (WB p.57) and adverbs of place (WB p. 47)
Here are some songs about adverbs:
lunes, 15 de febrero de 2016
Al-Andalus
What do you know about Al-Andalus?
Try this and see!
What do you need to know for the test?
Important dates:
711 AD
Here you can find out more about Art and Architecture in Al-Andalus.
Try this and see!
What do you need to know for the test?
Important dates:
711 AD
929 AD
1031 AD
Vocabulary:
Islam
Muslims
Koran
caliphate
caliphate
taifas
zoco
medina
alcazaba
arrabal
Other information:
Muslim contributions to:
--Mathematics
--Agriculture
--Craft and Industry
Name two examples of buildings in Spain from this time period:
--Mezquita (Mosque) of Córdoba
--The Alhambra of Granada
Here you can find out more about Art and Architecture in Al-Andalus.
jueves, 11 de febrero de 2016
Interaction in plants: Do sunflowers follow the sun?
Watch this video and listen to find your answer:
And here's another video:
And here's another video:
Next 15 verbs
Here are the next 15 verbs to study. We will have a test next week.
The last six verbs will be on the English test for Unit 6.
The last six verbs will be on the English test for Unit 6.
|
Simple
|
Past
|
Past Participle
|
|
say
|
said
|
said
|
|
see
|
saw
|
seen
|
|
sell
|
sold
|
sold
|
|
send
|
sent
|
sent
|
|
show
|
showed
|
shown
|
|
sit
|
sat
|
sat
|
|
sleep
|
slept
|
slept
|
|
speak
|
spoke
|
spoken
|
|
spend
|
spent
|
spent
|
|
stand
|
stood
|
stood
|
|
sweep
|
swept
|
swept
|
|
swim
|
swam
|
swum
|
|
take
|
took
|
taken
|
|
teach
|
taught
|
taught
|
|
tell
|
told
|
told
|
Parts of a cell
Do you know the parts of a cell?

Try this game and find out.
And this one: Label the animal cell
and: Label the plant cell
Cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
Test yourself!

Try this game and find out.
And this one: Label the animal cell
and: Label the plant cell
Cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
Test yourself!
miércoles, 10 de febrero de 2016
English games
I am going to add a tab to the blog so you can find the English games.
Let's start with these!
Speed Word
Basketball
Past simple questions
Past simple endings
More Games
-ed or -ing
Question words game
Write questions for these answers!
Here are all of the posts for English from this year. You can review the videos, songs, games, etc.
Let's start with these!
Past Simple games:
Speed Word
Basketball
Past simple questions
Past simple endings
Present Perfect games:
-ed or -ing
Question words game
Write questions for these answers!
Here are all of the posts for English from this year. You can review the videos, songs, games, etc.
lunes, 8 de febrero de 2016
Life processes in living things
Living things carry out three important life processes: interaction, nutrition, and reproduction.
Can you say which life process it is?






Can you say which life process it is?







Visigothic Spain
In your book you have a map of Roman influence in the Iberian peninsula (p. 88). But, in the 3rd century AD ( siglo III d.C.) the Roman Empire was in decline.
Roman Emperor Theodosius (Teodosio) divided the Roman Empire into two parts: The Western Roman Empire (capital in Rome) and the Eastern Roman Empire (capital in Constantinople.)
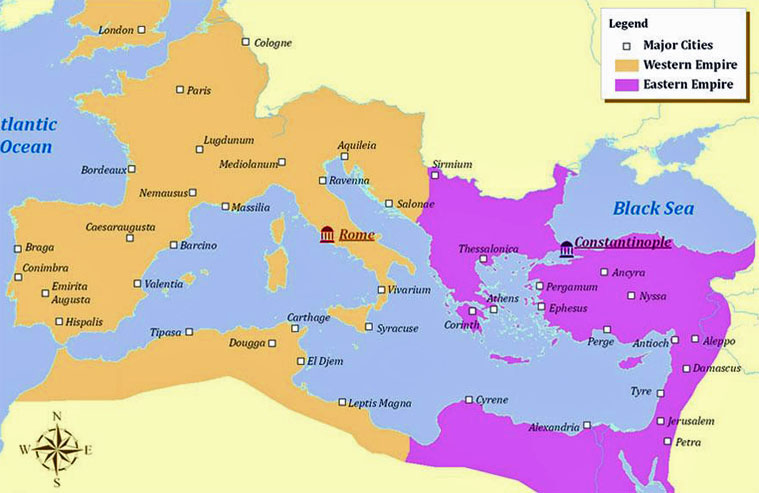
The Iberian Peninsula was invaded by Germanic tribes from the north and centre of Europe. In 409, the first Germanic tribes (the Romans called them "barbarians") arrived there: the Suebi (suevos), Vandals (vándalos), and Alans (alanos).

The Romans asked the Visigoths (visigodos) for help in 415 AD.
After the Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD, The Visigoths established a kingdom that stretched across the Pyrenees. It was called Toulouse (Tolosa.)

In 507, the Visigoths lost much of their kingdom and only kept the land they had in the Iberian peninsula. They set up their capital in Toledo. (See the map in your book on pg. 89.)
The Visigoths held on to (kept) much of Roman culture: they used the Latin language, and Roman law.
In 589, the Visigothic king Reccared (Recaredo) converted to Catholicism, and so did the rest of his country.

The church of San Juan de Baños, Palencia:

In 711, Muslim forces invaded and defeated the last Visigothic King, Roderic (Rodrigo), in the Battle of Guadalete. This began the period of Muslim domination of the Iberian Peninsula.
Roman Emperor Theodosius (Teodosio) divided the Roman Empire into two parts: The Western Roman Empire (capital in Rome) and the Eastern Roman Empire (capital in Constantinople.)

The Iberian Peninsula was invaded by Germanic tribes from the north and centre of Europe. In 409, the first Germanic tribes (the Romans called them "barbarians") arrived there: the Suebi (suevos), Vandals (vándalos), and Alans (alanos).

The Romans asked the Visigoths (visigodos) for help in 415 AD.
After the Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD, The Visigoths established a kingdom that stretched across the Pyrenees. It was called Toulouse (Tolosa.)

In 507, the Visigoths lost much of their kingdom and only kept the land they had in the Iberian peninsula. They set up their capital in Toledo. (See the map in your book on pg. 89.)
The Visigoths held on to (kept) much of Roman culture: they used the Latin language, and Roman law.
In 589, the Visigothic king Reccared (Recaredo) converted to Catholicism, and so did the rest of his country.

La conversión de Recaredo, por Antonio Muñoz Degrain, 1888.
Some important artifacts from the Visigothic Kingdom:
The Crown of Recesvinto from the treasure of Guarrazar:

See it in ·3D here:
The church of San Pedro Nave in Zamora:

Some important artifacts from the Visigothic Kingdom:
The Crown of Recesvinto from the treasure of Guarrazar:

See it in ·3D here:
The church of San Pedro Nave in Zamora:

The church of San Juan de Baños, Palencia:

In 711, Muslim forces invaded and defeated the last Visigothic King, Roderic (Rodrigo), in the Battle of Guadalete. This began the period of Muslim domination of the Iberian Peninsula.
sábado, 6 de febrero de 2016
viernes, 5 de febrero de 2016
jueves, 4 de febrero de 2016
miércoles, 3 de febrero de 2016
Art on Friday
For Art on Friday you need to bring oil pastels (pinturas de cera blanda tipo MANLEY o similar.)
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)






